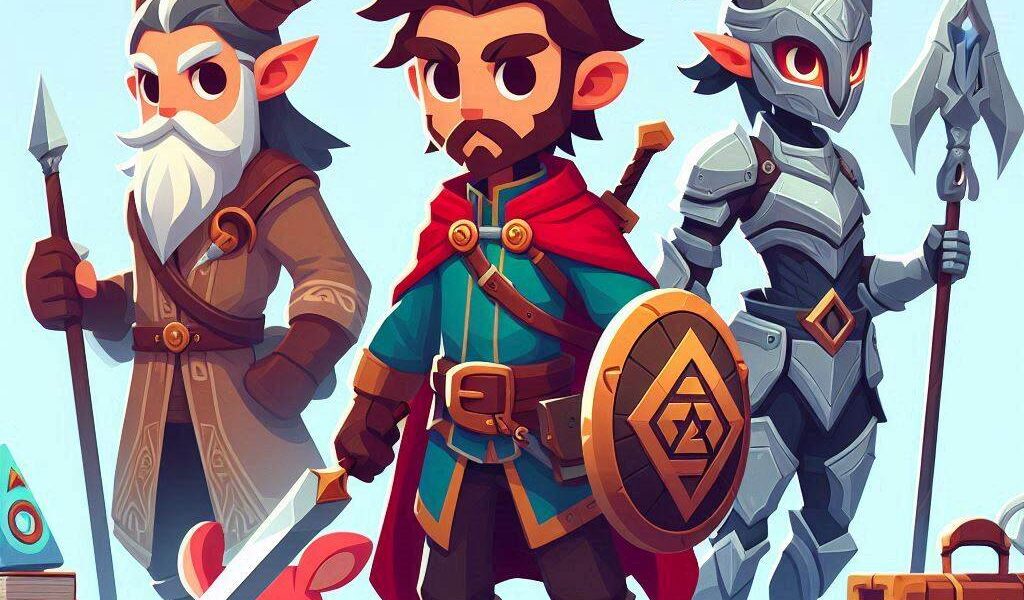
Unleash Your Imagination with Our Character Design Company
Are you looking to bring your characters to life with stunning, professional designs? Look no further than our character design company. At ServReality, we specialize in creating unique, detailed, and visually compelling characters that resonate with your audience and elevate your project to new heights.
Why Choose ServReality for Character Design?
Character design is more than just drawing; it’s about crafting a persona that connects with your audience on an emotional level. Whether it’s for a video game, animation, or any other digital platform, our experienced team at ServReality is equipped to transform your ideas into visually stunning and engaging characters.
- Customized Designs: Every project is unique, and so are our designs. We work closely with you to understand your vision and deliver characters that perfectly match your creative direction.
- Experienced Artists: Our team consists of skilled artists with extensive experience in the industry. They know how to blend creativity with technical expertise to produce characters that are not only visually striking but also functionally viable for any medium.
- Attention to Detail: We believe that every detail matters. From the smallest accessory to the character’s facial expression, we ensure that every element is meticulously designed to enhance the overall appeal.
- Versatility: Whether you need characters for a fantasy world, a futuristic sci-fi universe, or a modern-day setting, our artists have the versatility to adapt to any style or theme.
- Collaboration: We see our clients as partners. Throughout the design process, we maintain open communication to ensure that your vision is realized in every character we create.
Bring Your Characters to Life
In the world of digital entertainment, characters are often the heart and soul of the experience. A well-designed character can captivate your audience, drive engagement, and leave a lasting impression. At ServReality, we are passionate about delivering character designs that not only meet but exceed your expectations.
Ready to get started? Visit our https://servreality.com/game-art/character-design-company/ to learn more about our services and how we can help bring your characters to life.